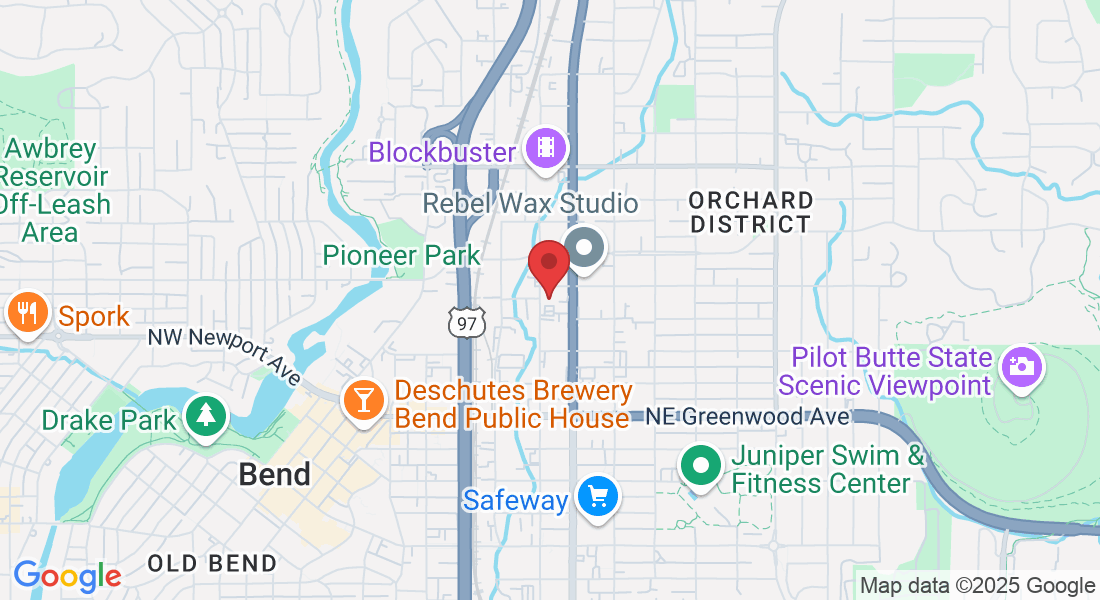
Shoulder Pain Relief
Rediscover Life Without Shoulder Pain
Renowned as a marvel of human anatomy, the shoulder joint offers unparalleled mobility and flexibility, enabling us to perform a myriad of tasks, from reaching out for a book on the top shelf to throwing the perfect spiral with a football. Yet, this exceptional range of motion comes at a price. Over time, instability or impingement of the soft tissues or bony structures in your shoulder may cause discomfort and pain. This pain might be transient or persisting, may manifest only when you move, or may be a constant presence, prompting the need for professional intervention.
We're pleased to share that minor shoulder pain frequently shows a promising response to strategies such as physical therapy, the use of shoulder supports, upholding a healthy lifestyle, all of which can bring about substantial relief. Here at PhysioFit, we comprehend that each person's journey to a pain-free life is distinct. We're dedicated to delivering personalized, science-backed treatments with a fitness-centric approach to effectively ease your shoulder discomfort, helping you return to your everyday activities.
What You Should Know
The human body's most versatile joint, the shoulder, owes its expansive motion range to a quartet of muscles and their corresponding tendons, collectively known as the rotator cuff.
Intriguingly, shoulder pain may sometimes be a symptom of an issue originating from another part of the body, such as the neck or lungs. This phenomenon, known as referred pain, typically presents as a persistent ache that doesn't worsen with shoulder movement.
Shoulder discomfort or pain can result from inflammation, injury, or bone alterations surrounding the rotator cuff.
A proper diagnosis of a shoulder problem involves a thorough evaluation from a professional
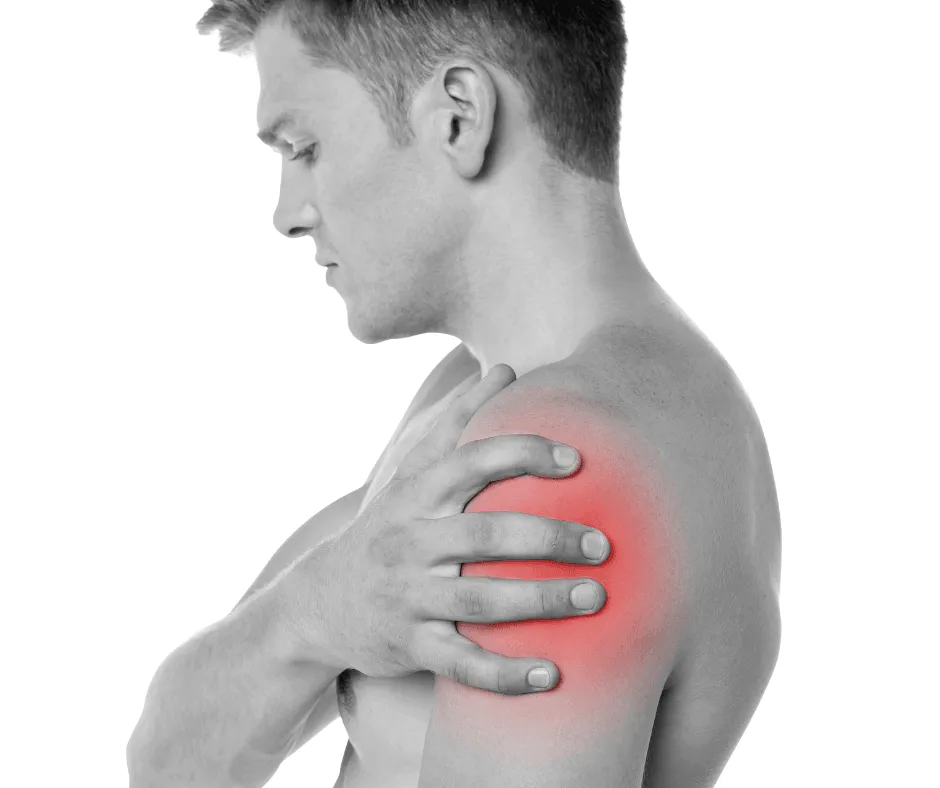
Understanding the Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
The shoulder is a complex joint, and it's susceptible to a variety of injuries and conditions. Here are some of the most common causes of shoulder pain:
Dislocation: This happens when the top of your arm is pulled back excessively or rotated too far, causing it to pop out of its socket. Symptoms include pain, weakness, swelling, numbness, and bruising in the shoulder.
Separation: This injury affects the acromioclavicular (AC) joint, where the collarbone and shoulder blade meet. A hard blow or fall can tear the ligaments, leading to a visible bump on top of your shoulder due to a displaced collarbone.
Fracture: A fall or severe blow can result in a broken or cracked bone. The clavicle (collarbone) and humerus (upper arm bone) are most prone to fractures, leading to intense pain, bruising, and restricted movement.
Cartilage Tear: Repeated motion, a fall, or a significant force can damage the cartilage that cushions your shoulder joint. Symptoms include pain during overhead reach, shoulder weakness, and a sensation of catching, locking, or grinding.
Rotator Cuff Tear: The group of muscles and tendons comprising your rotator cuff secure your arm in place and enable overhead lifting. Overuse, falls, or natural aging can cause damage, leading to pain (particularly at night), reduced lifting ability, and a crackling sound during movement.
Frozen Shoulder: Characterized by restricted joint movement, this condition is caused by the build-up of abnormal tissue bands (adhesions) within the joint, often following pain or surgery-induced disuse.
Impingement: This occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff are pinched between the shoulder bones, causing pain and swelling, particularly in individuals who frequently lift their arms overhead.
Bursitis: Overuse, repetitive motions, or an injury can inflame the bursa (a fluid-filled sac that cushions the joint), leading to pain, especially during shoulder movement.
Apart from these, other potential causes of shoulder pain include: Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Heart attack, Bone Spurs, Referred pain, and Tendinitis.
Remember, if you resonate with any of the symptoms or conditions mentioned, we highly recommend making an appointment with us for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Preventive Measures for Shoulder Pain
The bright side of shoulder issues is that they can often be resolved without resorting to surgery. However, prevention is always better than cure, and here are some ways you can safeguard your shoulders.
Heed Your Body's Signals: Do not dismiss shoulder discomfort that follows any activity. If the pain is intense and persistent, consult your doctor. Remember, enduring unnecessary pain might only exacerbate the situation.
Maintain Overall Health: Stay in prime physical condition with regular exercise and a balanced diet. It's not just a ticket to overall wellness, but it also helps in warding off potential injuries.
Adopt Correct Exercise Habits: Ensure a proper warm-up before your workouts. Gradually ease into a sport or activity if you've been inactive for a while. Learn and adhere to the correct techniques of weight lifting, and avoid lifting beyond your capacity.
Stay Safe at Work: Be conscious of your shoulder health in your work environment -
Prioritize good posture, whether you're sitting or standing.
Follow safe lifting practices. Maintain a straight back and leverage your leg strength.
Every hour, take a few minutes to move around and stretch.
If your job involves a desk, ensure your workstation is ergonomically set up for comfortable computer use.
Avoid Overreaching: When you need to access high places, use a step stool. Arrange frequently used items within easy reach, in lower drawers or shelves.
Remember, caring for your shoulder health can keep you active and pain-free in the long run.
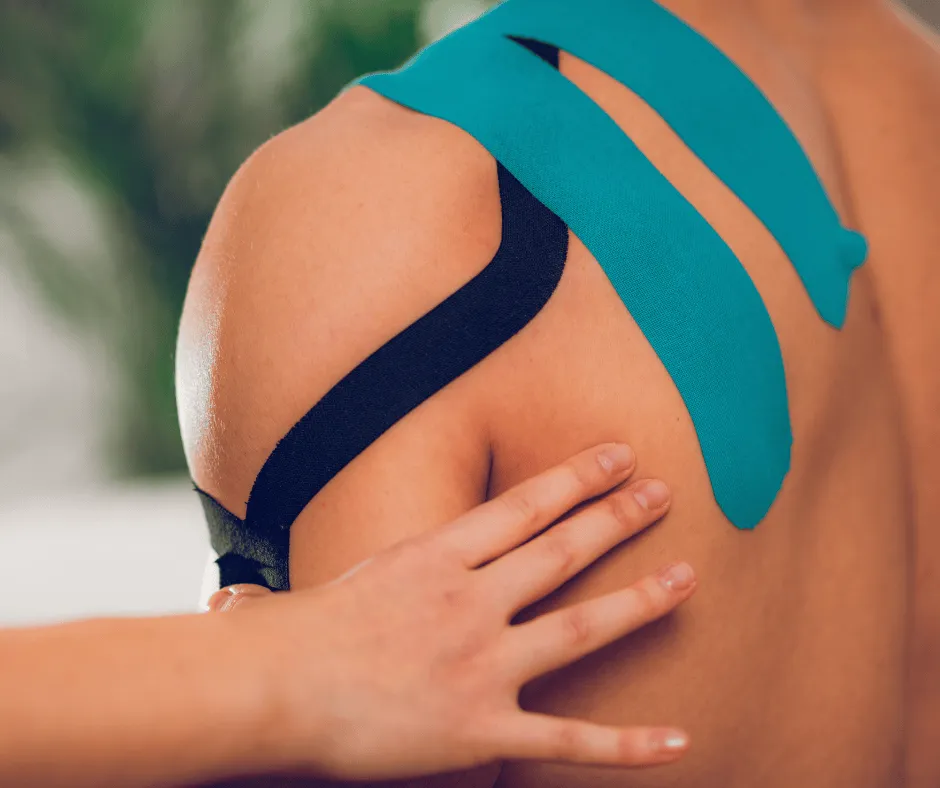
Common Symptoms of Shoulder Pain
Heat or a reddened appearance in your shoulder
Restricted arm mobility
Stiffness and reduced strength in your muscles
A sensation of clicking, popping, or grinding during arm movements
Discomfort in your neck, arm, or back
Remember, if you resonate with any of the symptoms or conditions mentioned, we highly recommend making an appointment with us for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Please Note: The information provided on our website is intended for general education and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Each individual's situation and body is different. Therefore, what may work for one person may not work for another. We care about your well-being and advise you to reach out to us to discuss your specific needs before implementing any advice from our website.
Your Source for All Things Physical Therapy in Bend Oregon
The PhysioBlog
Copyright PhysioFIT 2025 . All rights reserved